How PFAS Treatment Reduces Environmental Impact and Improves Public Safety
How PFAS Treatment Reduces Environmental Impact and Improves Public Safety
Blog Article
Advanced Approaches for Effective PFAS Contamination Elimination
The relentless challenge of PFAS contamination necessitates the exploration of advanced elimination approaches that can successfully attend to these hazardous compounds. Ingenious technologies, such as innovative oxidation procedures and various adsorption strategies, have emerged as appealing services in mitigating PFAS from influenced atmospheres.
Comprehending PFAS Residences
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) have been widely made use of in different industrial and customer products as a result of their special residential or commercial properties, their perseverance in the atmosphere presents significant difficulties to public health and safety. PFAS are a group of synthetic chemicals defined by a carbon-fluorine bond, one of the greatest chemical bonds recognized, which adds to their exceptional stability and resistance to deterioration. This security enables PFAS to accumulate in the environment and living microorganisms, resulting in potential negative wellness effects.
These exact same homes add to their ecological persistence, as PFAS do not conveniently damage down via all-natural procedures. Recognizing the chemical homes of PFAS is essential for creating efficient approaches to take care of and alleviate their ecological influence.
Ingenious Removal Technologies
The determination of PFAS in the setting has spurred the development of ingenious remediation innovations targeted at properly removing these contaminants from influenced environments. Among the most promising methods are sophisticated oxidation procedures (AOPs), which make use of powerful oxidants to break down PFAS substances right into less damaging substances. AOPs can be tailored to target particular PFAS frameworks, improving their effectiveness.
Another emerging technology is using adsorption media, such as triggered carbon and ion exchange materials, which can selectively record PFAS from contaminated water. These products have revealed substantial elimination performances, although routine substitute and regrowth are required to preserve efficiency.
Membrane layer filtering strategies, including reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are also obtaining traction in PFAS remediation. These techniques can successfully divide PFAS from water, offering a feasible service for dealing with infected sources. Furthermore, thermal therapy methods, such as incineration, can break down PFAS into non-toxic results, though they call for careful monitoring to manage discharges.
Collectively, these ingenious remediation innovations stand for significant developments in the continuous battle versus PFAS contamination, providing various approaches to restore afflicted environments and protect public wellness.
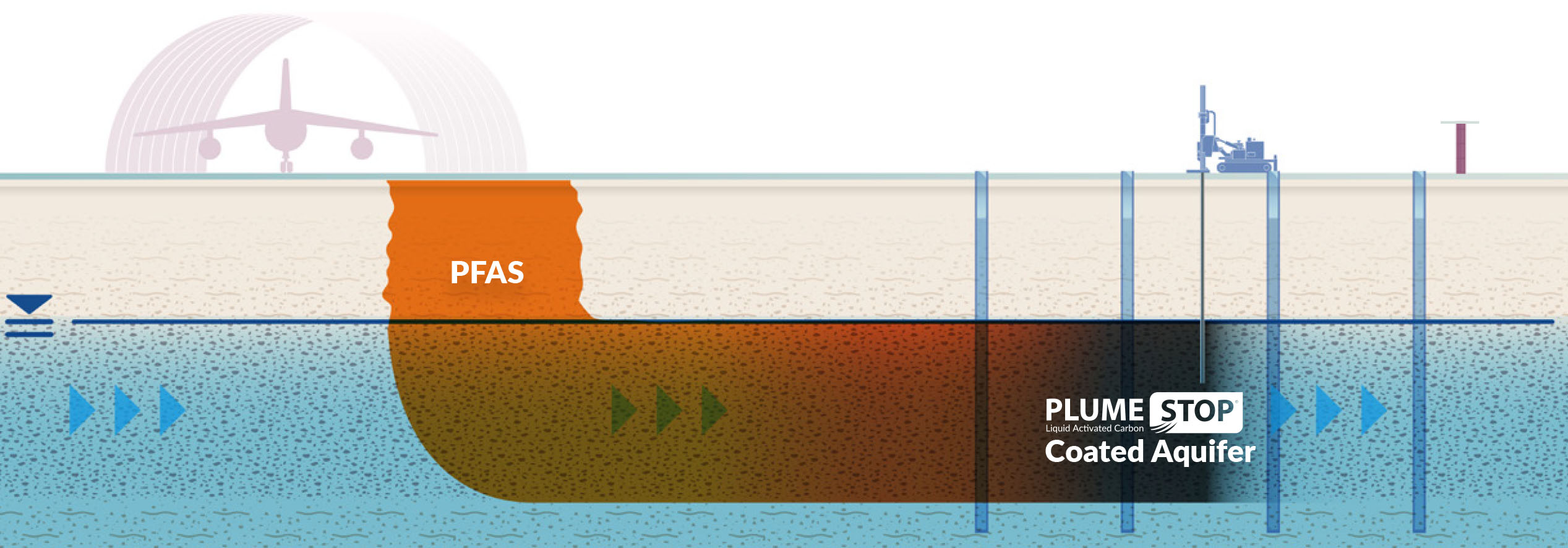
Bioremediation Techniques
Bioremediation techniques provide an encouraging method to dealing with PFAS contamination by taking advantage of the all-natural abilities of bacteria to degrade these persistent substances (m270 waste management). This approach entails the use of bacteria, fungis, and various other microorganisms that can metabolize or change PFAS substances into much less hazardous by-products
Recent advancements in molecular biology and environmental microbiology have actually enhanced our understanding of microbial neighborhoods and their possible roles in PFAS deterioration. Scientists are proactively exploring particular stress of microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have shown the ability to damage down certain PFAS substances.
Sitting bioremediation methods, where microbes are promoted straight in polluted settings, can be particularly efficient. This strategy frequently entails the application of nutrients or electron donors to advertise microbial growth and activity. Furthermore, ex situ approaches, such as bioreactors, permit regulated conditions that can maximize destruction This Site rates.
Regardless of the assurance of bioremediation, challenges stay, consisting of the intricate nature of PFAS compounds and the requirement for comprehensive area screening - m270 waste management. Continued r & d will certainly be essential to fine-tune these methods and analyze their efficiency in diverse ecological contexts
Adsorption and Purification Methods
Attending to PFAS contamination typically includes employing adsorption and filtering approaches, which are developed to get rid of these relentless chemicals from water and dirt. Among the different techniques, activated carbon adsorption is extensively utilized because of its high area and porosity, allowing effective capturing of PFAS particles. Granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems are specifically favored for treating big quantities of infected water, while powdered activated carbon (POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE) can be made use of for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange resins likewise reveal pledge in PFAS elimination, functioning by trading PFAS ions with much less dangerous ions in the water. This approach has shown efficiency in focusing PFAS compounds, facilitating their subsequent removal. In addition, membrane layer filtering strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, operate by utilizing semi-permeable membrane layers to separate PFAS link from water, efficiently minimizing their focus.
While these techniques are reliable, they must be very carefully picked based on the particular PFAS substances present and the ecological context. Constant advancements in materials scientific research and engineering are leading to the development of novel adsorbents and purification systems that boost removal performances and decrease operational expenses, thereby improving total removal initiatives.
Regulatory and Policy Factors To Consider
How can reliable regulative frameworks enhance the monitoring of PFAS contamination? Thorough policies are essential to ensure a collaborated and durable response to the challenges presented by per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) Laws can establish clear guidelines for tracking, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated websites, promoting accountability among markets and public entities. (m270 waste management)

Furthermore, monetary incentives and grants can be incorporated into plans to encourage the adoption of sophisticated removal technologies. Policymakers must also prioritize study and advancement, ensuring that arising approaches for PFAS removal are validated and implemented successfully.
Additionally, public understanding and involvement are important elements of any regulatory technique, encouraging communities to advocate for their health and wellness. Inevitably, a well-structured governing atmosphere will not just boost the monitoring of PFAS contamination but additionally advertise lasting practices that safeguard future generations.
Final Thought
In recap, the intricacy of PFAS contamination requires the adoption of sophisticated removal methods. Proceeded research study and advancement in this area stay essential to resolving the obstacles postured by see this PFAS contamination.
Report this page